For the second run, during sweeps the data were bootstrapped to construct a new dataset with the same sample size by sampling objects with replacement. On average, when randomly sampling objects with replacement during bootstrap construction of a dataset (i.e., each object is placed back into the pool of objects after random selection and can be sampled again), the probability that each object is not selected is 0.368, while the probability that each object is selected is 0.632. Bootstrapping is a commonly used technique in computer science for overcoming the challenge associated with not knowing if a dataset is reliable.
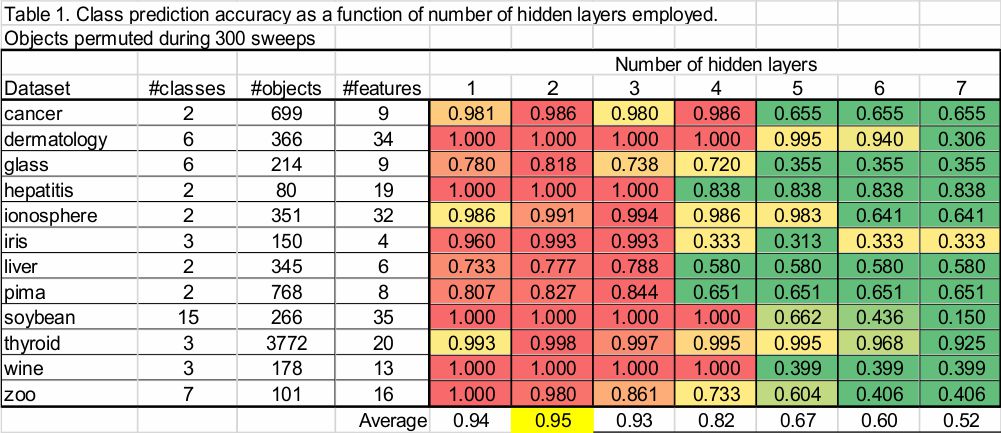
The ANN classification accuracy when bootstrapping during sweeps was similar to the results obtained when permuting objects during sweeps, in that class predictive accuracy dropped after more than 2 hidden layers were employed. Bootstrapping results also did not overestimate permutation results, suggesting the more conservativeness from bootstrapping.